
Publications
78 D’Onofrio, B.; Cruché, C.; Hurdal, K. N.; Hadjabdelhafid-Parisien, A.; Pelletier, J. N.; Iftimie, R. I.; Davis, R. L.; Collins, S. K. TPDYs: A Modular Platform for Bioconjugation Processes Employing Strained Macrocyclic Diynes. Chem. Commun. 2024, Advance Article

77 Beaucage, N.; Singh, Z.; Bourdon, J.; Collins, S. K. Tuning Co-Operative Energy Transfer in Copper(I) Complexes Using Two-Photon Absorbing Diimine-Based Ligand Sensitizers. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2024, e202412606

76 Guerrero-Morales, J.; Collins, S. K. Biocatalysis as a versatile tool for macrolactonization: comparative evaluation of catalytic and stoichiometric approaches. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 10404-10410.

75 Roland, G.; Hurdal, K. N.; Bouchouicha, A.; Dowe, N.; Davis, R. L.; Collins, S. K. [2+2] Photocycloadditions to form Cyclobutanes and Bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes Employing Copper-Based Photocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2024, 15, 11490–11497

74 Guerrero-Morales, J.; Scaglia, M.; Fauran, E.; Lepage, G.; Collins, S. K. Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Macrocycles via Dynamic Kinetic Resolution. Nature Synth. 2024, 3, 1275–1282.

73 Morin, É.; Neiderer, W.; Cruché, C.; Bleton, O.; Cave, C.; Collins, S. K. A Flow Chemistry Platform for Photochemical Macrocyclization of Peptides. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 6433–6439.

72 Bleton, O.; Beaucage, N.; Guerrero-Morales, J.; Collins, S. K. Photocatalytic Thiol–Yne Reactions of Alkynyl SulfidesJ. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 17257–17265.

71 Clémentine Minozzi, C.; Dowe, N.; Beaucage, N.; Collins, S. K. Chemoenzymatic Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Secondary Alcohols and Amines Employing Copper-Based Photocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 8347–8353.

70 Cruché, C.; Gupta, S.; Kodanko, J.; Collins, S. K. Heteroleptic Copper(I)-Based Complexes Incorporating BINAP and p-Extended Diimines: Synthesis, Catalysis and Biological Applications. Molecules. 2022, 27, 3745-3753.

69 Bertin, C.; Cruché, C.; Chacon-Huete, F.; Forgione, P.; Collins, S. K. Decomposition of Lignin Models Enabled by Copper-Based Photocatalysis Under Biphasic Conditions. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 4414-4419.

68 Cruché, C.; Neiderer, W.; Collins, S. K. Heteroleptic Copper-Based Complexes for Energy-Transfer Processes: E → Z Isomerization and Tandem Photocatalytic Sequences. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 8829–8836

67 Morency, M.; Iftimie, R. I.; Collins, S. K. Computational Insight into a Cu-Catalyzed Csp-S Coupling to Form a Macrocyclic Alkynyl Sulfide, J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 5120–5128

66 Kairouz, V.; Charette, A. B.; Collins, S. K. Implementing Flow Chemistry in Education: The NSERC CREATE Program in Continuous Flow Science, J. Flow Chem. 2021, 11. 13-17.

65 Godin, É.; Nguyen Thanh, S.; Guerrero-Morales, J.; Santandrea, J.; Caron, A.; Minozzi, C.; Beaucage, N.; Rey, B.; Morency, M.; Abel-Snape, X.; Collins, S. K. Synthesis and Diversification of Macrocyclic Alkynediyl Sulfide Peptides, Chem- Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14575-14579.

64 Santandrea, J.; Godin, E.; Collins, S. K A Synthetic Guide to Alkynyl Sulfides Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 4885-4893.

63 Godin, E.; Santandrea, J.; Caron, A.; Collins, S. K General Cu-Catalyzed Csp-S Coupling, Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 5905-5909.

62 Sosoe, J.; Cruché, C.; Morin, É.; Collins, S. K. Evaluating Heteroleptic Copper(I)-Based Complexes Bearing π-Extended Diimines in Different Photocatalytic Processes, Can. J. Chem. 2020, 48, 461-465

61 Gagnon, C.; Godin, E.; Minozzi, C.; Sosoe, J.; Pochet, C.; Collins, S. K. Biocatalytic Synthesis of Planar Chiral Macrocycles, Science 2020, 367, 917-921.

60 Caron, A.; Morin, É.; Collins, S. K. Bifunctional Copper-Based Photocatalyst for Reductive Pinacol-Type Couplings. ACS Catal. 2019, 10, 9458-9464.

59 Grenier-Petel, J.-C. Collins, S. K. Photochemical Cobalt-Catalyzed Hydroalkynylation to Form 1,3-Enynes. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3213–3218.

58 Morin, E.; Sosoe, J.; Raymond, M.; Boden, R.; Amorelli, B.; Collins, S. K. Synthesis of a Renewable Macrocyclic Musk: Evaluation of Batch, Microwave and Continuous Flow Strategies. Org. Process Reac. Dev. 2019, 23, 283–287.

57 Parisien-Collette, S.; Collins, S. K. Exploiting Photochemical Processes in Multi-Step Continuous Flow: Derivatization of the Natural Product Clausine C ChemPhotoChem 2018, 2, 855-859.

56 Minozzi, C.; Grenier-Petel, J.-C.; Parisien-Collette, S.; Collins, S. K Photocatalyic Appel Reaction Enabled by Copper-Based Complexes in Continuous Flow Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2730–2736.

55 Minozzi, C.; Caron, A.; Grenier-Petel, J.-C.; Collins, S. K. Heteroleptic Copper(I)-Based Complexes for Photocatalysis: Combinatorial Assembly, Discovery, and Optimization Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5477-5481.

54 Santandrea, J.; Kairouz, V.; Collins, S. K. Continuous Flow Science in an Undergraduate Teaching Laboratory: Photocatalytic Thiol–Ene Reaction Using Visible Light J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 95, 1073–1077.

53 Godin, É.; Morin, É.; Collins, S. K. Continuous Flow Macrocyclization Aldrichimica Acta. 2018, 51, 35-46.
52 Parisien-Collette, S.; Cruché, C.; Abel-Snape, X.; Collins, S. K. Photochemical Intramolecular Amination for the Synthesis of Heterocycles Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4798-4803.

51 Santandrea, J.; Minozzi, C.; Cruché, C.; Collins, S. K. Photocatalytic Synthesis of Alkynyl Sulfides Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12255–12259.

50 Godin, É.; Bédard, A.-C.; Raymond, M.; Collins, S. K. Phase Separation Macrocyclization in a Complex Pharmaceutical Setting: Application Towards the Synthesis of Vaniprevir J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 7576–7582.

49 Kairouz, V.; Collins, S. K. Continuous Flow Science in an Undergraduate Teaching Laboratory: Bleach-Mediated Oxidation in a Biphasic System J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 95, 1069-1072.

48 Morin, É.; Raymond, M.; Dubart, A.; Collins, S. K. Total Synthesis of Neomarchantin A: Key Bond Constructions Performed Using Continuous Flow Methods. Org.Lett. 2017, 19, 2889-2892.

47 Hernandez-Perez, A. C.; Collins, S. K. Heteroleptic Cu-Based Sensitizers in Photoredox Catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1557-1565.

46 de Léséleuc, M; Godin, E.; Parisien-Collette, S.; Lévesque, A.; Collins, S. K. Catalytic Macrocyclization Strategies Using Continuous Flow: Formal Total Synthesis of Ivorenolide A. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 6750-6756.

45 Parisien-Collette, S.; Hernandez-Perez, A. C.; Collins, S. K. Photochemical Oxidation Using a Fe(phen)3(NTf2)2/O2 Catalyst System. Org.Lett. 2016, 18, 4994-4997.
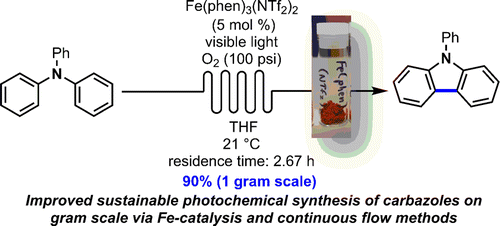
44 Hernandez-Perez, A.; Caron, A.; Collins, S. K. Photochemical Synthesis of Complex Carbazoles: Evaluation of Electronic Effects in Both UV- and Visible-Light Methods in Continuous Flow. Chem Eur J. 2015, 16673-16678.

43 de Léséleuc, M.; Collins, S. K. Direct Synthesis of Macrodiolides via Hafnium(IV) Catalysis. Chem Commun. 2015, 51, 10471-10474.

42 Bédard, A.-C.; Santandrea, J.; Collins, S. K. Efficient Continuous Flow Synthesis of Macrocyclic Triazoles. J. Flow Chem. 2015, 3. 142-144

41 de Léséleuc, M.; Collins, S. K. Direct Macrolactonization of Seco Acids via Hafnium(IV) Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1462-1467.

40 Caron, A.; Hernandez-Perez, A. C.; Collins, S. K. A Continuous Flow Reactor for UV-Light Mediated Synthesis. Org. Proc. Reac. Dev. 2014, 1571-1574.

39 Santandrea, J.; Bédard, A.-C.; Collins, S. K. Macrocyclic Cu(I)-Catalyzed Sonogashira Cross-Coupling. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3892-3895.

38 Raymond, M.; Holtz-Mulholland, M.; Collins, S. K. Macrocyclic Olefin Metathesis at High Concentrations Using a Phase Separation Strategy. Chem Eur. J. 2014, 20, 12763–12767.

37 Bédard, A.-C.; Collins, S. K. Efficient Macrocyclic Cu(I)-Catalyzed Cycloaddition of Iodoalkynes and Azides via a Phase Separation Strategy. Org. Lett. 2014, 15, 5286-5289.

36 Bédard, A.-C.; Vlassova, A.; Hernandez-Perez, A. C.; Bessette, A.; Hanan, G. S.; Heuft, M. A.; Collins, S. K. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Photophysical Properties of Pyrene/Helicene Hybrids. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 16295-16302.

35 Hernandez-Perez, A. C.; Collins, S. K. A Visible Light Mediated Synthesis of Carbazoles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12696-12700.

34 Holtz-Mulholland, M.; Collins, S. K. Synthesis of Chiral C1-Symmetric N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands: Application Toward Copper-Catalyzed Homocoupling of 2-Naphthols. Synthesis 2013, 24, 375-380.

33 Bédard, A.-C.; Regnier, S.; Collins, S. K. Continuous-Flow Macrocyclization at High Concentrations: Synthesis of Macrocyclic Lipids. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1962-1966.

32 Bédard, A.-C.; Collins, S. K. Influence of Poly(Ethylene)Glycol Structure on Catalytic Macrocyclization Reactions. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 773-782.

31 Holtz-Mulholland, M.; de Léséleuc, M.; Collins, S. K. Heterocoupling of 2-Naphthols Enabled by a Copper/N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complex. Chem. Comm. 2013, 1835-1837.

30 Bédard, A.-C.; Collins, S. K. Exploiting Aggregation to Achieve Phase Separation in Macrocyclization. Chem. Eur.–J. 2013, 19, 2108-2113.

29 Hernandez-Perez, A. C.; Vlassova, A.; Collins, S. K. Toward a Visible Light Mediated Photocyclization: Cu-Based Sensitizers for the Synthesis of [5]Helicene. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 2988-2991.

28 Bédard, A.-C.; Collins, S. K. Microwave Accelerated Glaser-Hay Macrocyclizations at High Concentrations. Chem. Comm. 2012, 6420-6422.

27 Bédard, A.-C.; Collins, S. K. Phase Separation as a Strategy Towards Controlling Dilution Effects in Macrocyclic Glaser-Hay Couplings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19976-19981.

26 LeGall, T.; Baltatu, S.; Collins, S. K. Synthesis of Mono- and Bis-N-Heterocyclic Carbene Cu(I) Complexes via Decarboxylative Generation of Carbenes. Synthesis 2011, 22, 3687-3691.

25 Bolduc, P.; Jacques, A.; Collins, S. K. Efficient Macrocyclization Achieved via Conformational Control Using Intermolecular Noncovalent π-Cation/Arene Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12790-12791.

24 Dubois, M.-A.; Grandbois, A.; Collins, S. K.; Schmitzer, A. R. Introduction of Axial Chirality in a Planar Aromatic Ligand Results in Chiral Recognition with DNA J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 288-294.
23 Stenne, B.; Timperio, J; Savoie, J.; Dudding, T.; Collins, S. K. Desymmetrizations Forming Tetrasubstituted Olefins Using Enantioselective Olefin Metathesis Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 2032–2035.

22 Grandbois, A.; Mayer, M.-E.; Bédard, M.; Collins, S. K.; Michel, T. Synthesis of C1-Symmetric BINOLs Employing N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Copper Complexes. Chem. Eur.–J. 2009, 15, 9655-9659.

21 Savoie, J.; Stenne, B.; Collins, S. K. Improved Chiral Olefin Metathesis Catalysts: Increasing the Thermal and Solution Stability via Modification of a C1-Symmetric N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligand. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 1826-1832.

20 Côté. J.; Collins, S. K. Synthesis of Higher Helicenes via Olefin Metathesis and C-H Activation, Synthesis 2009, 1499-1505.

19 El-Azizi, Y.; Zakarian, J. E.; Bouillerand, L.; Schmitzer, A. R.; Collins, S. K. Efficient Macrocyclizations via Metathesis Employing Amide-Based Auxiliaries, Adv. Synth. Cat. 2008 350, 2219-2225

18 Grandbois, A.; Collins, S. K. Enantioselective Synthesis of [7]Helicene: Simple Olefins as Additives in Asymmetric Olefin Metathesis, Chem. Eur.–J. 2008, 14, 9323-9329.

17 Zakarian, J. E.; El-Azizi, Y.; Collins, S. K. Exploiting Quadrupolar Interactions in the Synthesis of the Macrocyclic Portion of Longithorone C, Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2927-2930.

16 Fournier, P.-A.; Savoie, J.; Bédard, M.; Stenne, B.; Grandbois, A.; Collins, S. K. Mechanistically Inspired Catalysts for Enantioselective Desymmetrizations via Olefin Metathesis, Chem.–Eur. J. 2008, 14, 8690-8695.

15 Collins, S.K.; El-Azizi, Y.; Schmitzer, A., Development of Perfluoroarene:Arene Interactions for Macrocyclic En-Yne Metathesis and the Total Synthesis of Macrocyclic Natural Products, J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 6397- 6408.

14 Collins, S.K.; Fournier, P.-A., A Highly Active Chiral Ru-based Catalyst for Enantioselective Olefin Metathesis, Organometallics 2007, 26, 2945-2949.

13 Collins, S.K., Preparation of Cyclic Molecules Bearing "Strained Olefins" Using Olefin Metathesis, J. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 691, 5122-5128.

12 Collins, S.K.; Vachon, M. P. Unlocking the Potential of Thiaheterohelicenes: Chemical Synthesis as the Key. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 2518-2524.

11 Collins, S. K.; Grandbois, A.; Vachon, M. P.; Côté, J. Olefin Metathesis as a Route to Helicenes, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2923 - 2926.

10 Collins, S. K.; El-azizi, Y. Development of Quadrupolar Engaging Auxiliaries for Macrocyclization, Pure App. Chem. 2006, 78, 783-789.
9 Collins, S.K.; El-azizi, Y.; Schmitzer, A. Exploiting Perfluorophenyl-Phenyl Interactions for Achieving Difficult Macrocyclizations using Ring Closing Metathesis, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 968-973.

8 Bewley, C. A.; Ray, S.; Cohen, F.; Collins, S. K.; Overman, L. E. Inhibition of HIV-1 Envelope-Mediated Fusion by Synthetic Batzelladine Analgues, J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1319 – 1324.
7 Collins, S. K.; McDonald, A. I.; Overman, L. E.; Rhee, Y. H. Enantioselective Synthesis of (-)-Dehydrobatzelladine C, Org Lett. 2004, 6, 1253- 1255.
6 Cohen, F.; Collins, S.K.; Overman, L.E., Assembling Bis-Polycyclic Guanidinium Motifs Resembling Batzelladine Alkaloids by Double Tethered Biginelli Condensations, Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 4485– 4488.
5 Heuft, M.A., Collins, S.K.; Fallis, A.G., Molecular Folding of C60 Acetylenic Cyclophanes: p-Stacking of Superimposed Aromatic Rings, Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1911- 1914.
4 Collins, S. K.; Yap, G. P. A.; Fallis, A. G., A Novel Strained Undecadiyne Cyclophane with Interesting Dienophilic Character, Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 11-14.
3 Heuft, M.A.; Collins, S.K.; Yap, G.P.A.; Fallis, A.G., Synthesis of Diynes and Tetraynes from in-situ Desilylation/Dimerization of Acetylenes, Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 2883-2886.
2 Collins, S.K.; Yap, G.P.A.; Fallis, A.G., Synthesis of Novel Acetylenic Cyclophanes with Helical Chirality: Potential New Structures for Liquid Crystals, Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 3189- 3192.
1 Collins, S.K., Yap G.P.A., and Fallis A.G., The Synthesis of a Novel Strained Diyneparacyclophane and its Dimer by Metal Mediated Coupling, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2000, 39, 385.
Book Chapters
21. Santandrea, J.; Bédard, A.-C.; de Léséleuc, M.; Raymond, M.; Collins, S. K. Alternative Synthetic Strategies to Macrocycles in Practical Medicinal Chemistry with Macrocycles, Wiley (Eds. Marsault, E.; Peterson, M.) 2017 .
20. Holtz-Mulholland, M.; Collins, S. K. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Asymmetric Transition Metal Catalysis in N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Catalytic Organic Synthesis 2 (Science of Synthesis),Georg Thieme Verlag KG, Stuttgart, New York (Eds. Nolan, S. P.; Cazin, C. S. J.) 2017, 229-264
19. Godin, É.; Collins, S. K. Di-n-butyl Phosphate, eROS, 2016
18. Morin, É.; Collins, S. K. Bis(benzyloxy)methane, eROS, 2016
17. Minozzi, C.; Collins, S. K. Di-tert-butyl chloromethyl phosphate, eROS, 2016
16. Parisien-Collette, S.; Collins, S. K. 2-Amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol, eROS, 2016
15. Parisien-Collette, S.; Collins, S. K. 1,2-benzodiazine, eROS, 2014
14. Caron, A.; Collins, S. K. Quinoline, eROS, 2014
13. Santandrea, J.; Collins, S. K. Benzotriazole, eROS, 2014
12. Parisien-Collette, S.; Collins, S. K. 2-Amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol, eROS, 2014
11. Bédard, A.-C.; Collins, S. K. Iridium, tris[2-(2-pyridinyl-KN)phenyl-KC]-, (OC-6-22)-iridium, eROS, 2014
10. Raymond, M.; Collins, S. K. Dichloro[1,3-bis(2-methylphenyl)-2-imidazolidinylidene](2-isopropoxyphenylmethylene) ruthenium(II) (Stewart-Grubbs Catalyst), eROS, 2014
9. Hernandez-Perez, A. C.; Collins, S. K. Cu(Xantphos)(dmp)BF4, eROS, 2014
8. Holtz-Mulholland, M.; Collins, S. K. 1,3-Dihydro-1,3-bis(tricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]dec-1-yl)-2H-imidazol-2-ylidene, eROS, 2013.
7. Collins, S. K. Solvent and Additive Effects in Olefin Metathesis in Handbook of Metathesis Volume 2, Wiley (Eds Grubbs, R. H.; Wenzel, A. G.). 2013, 343-375.
6. Stenne, B.; Collins, S. K. Enantioselective Metathesis in Olefin Metathesis & Practice, Wiley (Eds Grela, K.) 2013, 233-267.
5. LeGall T.; Collins, S. K. 1-Mesityl-3,4-dimethyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium tetrafluoroborate, eROS, 2012.
4. Holtz-Mulholland, M.; Collins, S. K. 3-(2,4,6-Trimethylphenyl)-1-methyl-1-H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium Iodide, eROS, 2012.
3. Collins, S. K. 1,4-Dimethyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium iodide, eROS, 2011.
2. Collins, S. K. Enantioselective and Diastereoselective Metathesis, Science of Synthesis, 2011, 1, 819-871.
1. Holtz-Mulholland, M.; Collins, S. K. Ruthenium, [(4R,5R)-4,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1-[5-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-methoxy-2-(1-methylethyl)phenyl]-3-methyl-2-imidazolidinylidene]dichloro(phenylmethylene)(tricyclohexylphosphine)], eROS, 2011.